We are all aware of the long history of the development of uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. UPS’s continuing product updates will usher in a historic change.
We’ve all used lead-acid batteries as backup power and paired them with UPS systems in the past. However, because of the rapid development of lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries are gradually being phased out. What’s more frightening is that this is an irrevocable imagination. To put it another way, lithium batteries will someday completely replace lead-acid batteries.
The market application where lithium batteries are now replacing lead-acid batteries is mostly low-voltage solutions. The lithium ups batteries have a voltage range of 48V to 480V, and it will be much higher in the future.
In this post, you will learn more about lithium-ion batteries and their role in UPS energy storage in the future.
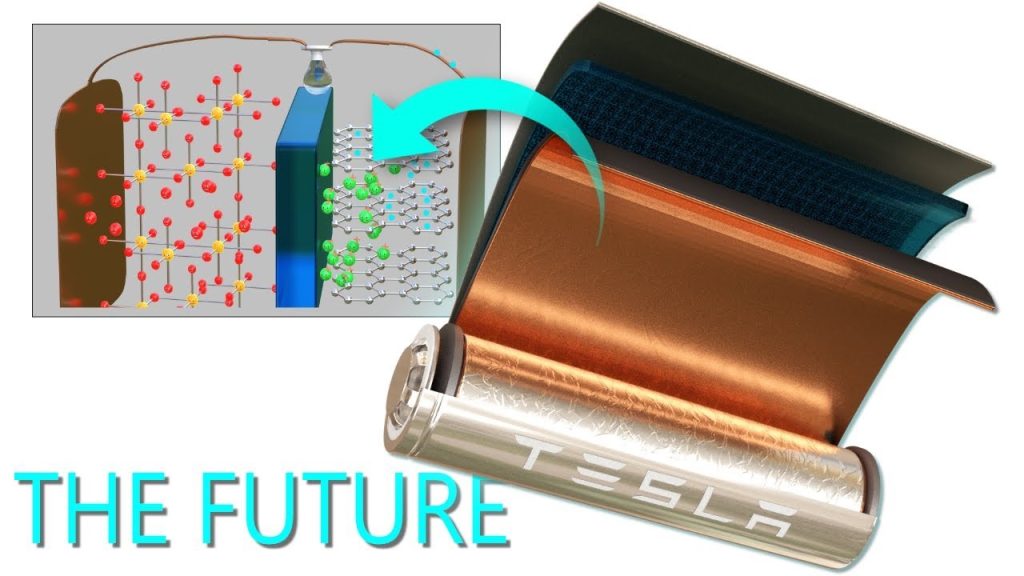
What exactly is a lithium-ion battery and what qualities does it have?
A lithium-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that charges and discharges by moving lithium ions between the negative (anode) and positive (cathode) electrodes. (Secondary batteries are those that can be charged and discharged again, whereas primary batteries are those that are disposable.)
Because lithium-ion batteries can store enormous amounts of power, they are used in a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics such as smartphones and PCs, industrial robots, manufacturing equipment, and automobiles.
What is the capacity of lithium-ion batteries to store energy?
A lithium-ion battery is composed of three components:
1) the anode and cathode;
2) a separator between the two electrodes; and
3) an electrolyte that occupies the remaining space in the battery.
Lithium ions can be stored in both the anode and the cathode. Energy is stored and released as lithium ions move between these electrodes through the electrolyte.
What Is UPS Exactly?
The term UPS stands for uninterruptible power supply. This physical component also serves as a backup power supply. As the name suggests, UPS controls a constant supply of electricity.
When there is a significant decline in power or a complete loss of power, UPS can assist. This is because of the UPS’s several batteries. It can detect such a loss or dip in the major power.
As a result, the UPS provides backup power with a power loss. This device is vital, especially while working on a computer and the power goes off. It allows people to save work and turn off computers by providing enough emergency power. Most UPS manufacturers used to make lead-acid battery UPS that only used lead-acid batteries for backup power. Lithium-ion battery ups have lately appeared in response to the increase in lithium-ion batteries. Most people expect that lithium-ion battery backups will become increasingly important in the future.
Is it possible to use lithium batteries in UPS?
Yes, lithium-ion batteries may be used in UPS systems. But don’t get lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries mixed up. There are two kinds of batteries.
The first cannot be recharged, although the second can. Lithium batteries are expected to last up to four times as long as lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries cost less than lithium-ion batteries. They are also smaller and lighter than other battery kinds. They last longer and do not require any form of ventilation to work correctly.
Lithium batteries outperform other types of batteries in terms of dependability. They include a sophisticated monitoring or management system.
Lithium batteries have just recently been employed in electric vehicles. So, when those enormous automobiles start moving. It will surely help you at home and in your business. Most take up less space or operate at a slower rate than other batteries.

What are the primary benefits of utilizing lithium-ion UPS batteries?
The most frequently claimed reason is the significantly longer service life. Lithium-ion batteries also offer a longer warranty and a higher cycle life (the number of charge/discharge cycles ranges from thousands to tens of thousands against roughly 500 for VRLA batteries). The lighter weight and smaller footprint are advantages.
IT managers may deploy lithium-ion UPSs fast without the maintenance and refresh issues that plague lead acid UPSs. Customers may plan their UPS refresh cycles with the rest of the IT stack since lithium-ion batteries have a longer battery life, saving time and money on labour and new batteries. Lithium-ion UPSs offer a “put it and forget it” value proposition, which is useful in regions where UPSs protect critical network operations but IT resources are restricted.
Is a Lithium Battery a good long-term investment for UPS energy storage?
A lithium battery is a better value than a normal sealed lead-acid battery. VRLA batteries have various disadvantages, such as shorter cycle life, higher maintenance costs, and being heavier than UPS lithium-ion batteries. Lithium batteries are the best option for providing continuous power, safety, consistency, and longevity.

Lithium batteries for backup power systems will be a prominent topic in the future.
Here are some advantages of buying a lithium battery.
A greater power density saves space.
Lithium-ion batteries UPS batteries have a higher power density and recharge faster than SLA batteries. They are smaller and lighter, making better use of space. For example, providing extra server rooms, IT equipment, and future power improvements.
Increases the power system’s availability.
The Lithium-ion battery UPS is made using innovative technology and has an interactive control system. It allows for individual and precise cell monitoring, reducing the chance of battery failure.
BMS, sensors, switches, microprocessors, and related circuits are key components of a battery system, increasing the cost while decreasing the risk. Temperature, charge level, and voltage level are all monitored by the BMS to prevent discharge from dropping too low and to prevent overcharging.
Replacement expenses decrease as life expectancy rises.
Lithium-ion battery-powered UPS is less sensitive to high temperatures and requires less cooling. In terms of cycle life and battery life, it outlasts lead-acid batteries. It reduces the cost of replacements, maintenance, and energy. Isn’t it worthwhile to buy?
Disposals are risk-free.
Battery manufacturers are developing more environmentally friendly choices to reduce their environmental impact. It does not contain any dangerous substances like mercury, lead, or cadmium produces no fumes and has no risk of acid leakage. As a result, the state of California has determined that they are safe for landfill disposal.
All battery types that involve chemical energy can be harmful if not handled properly or overcharged. The same is true with lithium-ion batteries, which, if not handled properly, can create a fire or thermal runaway.
However, there is no need to be afraid because significant development and cell packaging breakthroughs in lithium-ion battery safety have been made. The materials used are long-lasting, and the battery has undergone extensive testing. Are you secure now that you use portable electronics, telephones, and electric automobiles that all contain lithium batteries?
Recyclable
Many recyclers gather smaller lithium-ion batteries and send them to be burned to recover a portion of the waste components. However, much of the garbage ends up in landfills, where it has little influence on the environment.
Because larger lithium batteries used in data centre UPS are more difficult to recycle because of PCB boards and other electronics, research on proper battery recycling is ongoing. Because of the predicted increase in UPS batteries, recycling businesses have increased their efforts to recycle larger batteries.

Final Thoughts
Lithium-ion batteries, which are extensively used in consumer electronics, are increasingly being used as a backup energy source for Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) in data centres.
In UPS applications, lithium-ion batteries can save 10-30% on TCO over lead-acid batteries during a 15-year UPS system life. While the initial capital cost is slightly higher than lead-acid batteries, the lower operational expenses can cause significant TCO savings.
They often have a longer expected lifespan and cycle life, are smaller and lighter, and can operate at higher temperatures. Lithium-ion batteries require less maintenance and are less hazardous to the environment than lead-acid batteries.
They will play a considerably larger part in UPS applications in the next years. Data centre owners and colocation providers will have a more secure power infrastructure because of the deployment of embedded blockchain technology in lithium-ion battery Management Systems (BMS).














